The Indian Air Force Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) Competition, also known as the MRCA tender, is an ongoing competition to supply the Indian Air Force (IAF) with 126 multi-role combat aircraft. The Defence Ministry has allocated  42,000 crore (US$9.32 billion) for the purchase of these aircraft,
42,000 crore (US$9.32 billion) for the purchase of these aircraft, making it India's single largest defence deal.
Bidders
Six aircraft were bid for the order – the Swedish Saab Gripen, Eurofighter Typhoon, French Dassault Rafale, Russian Mikoyan MiG-35, and the American F-16IN and F/A-18IN Super Hornet ("IN" are the proposed Indian versions). Previously, Mikoyan and Dassault have been regular suppliers of aircraft for the Indian Air Force and in terms of transfers of technology, licensed production in India, personnel training, supply of spare parts, maintenance and upgrading.
IAF pilots and technicians are familiar with earlier aircraft from those two aircraft manufacturers, and would need minimal retraining. Infrastructural and logistical support for maintenance and spares would also be easier for these aircraft compared to the unfamiliar Gripen, Typhoon, F-16 and F/A-18.
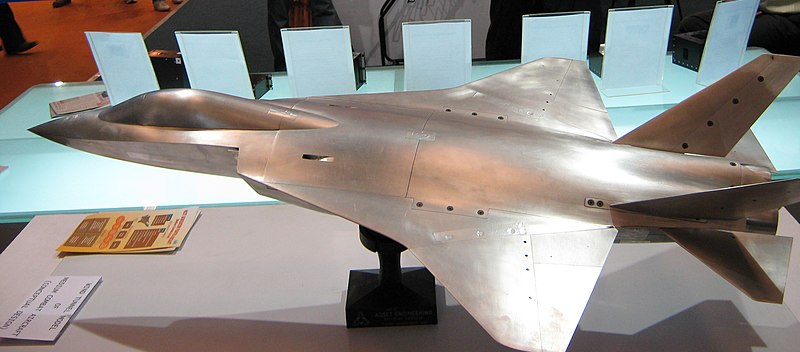
Dassault Rafale

Dassault Rafale
The Dassault Rafale is a French twin-engined delta-wing agile multi-role fighter aircraft designed and built by Dassault Aviation. The Rafale was brought in as the replacement for the Mirage 2000-5 that was originally a competitor for the tender,
after the production lines for the Mirage closed down, as well as the entry of much more advanced aircraft into the competition. The fighter also has the Rafale M variant for carrier-based use.
The Rafale has the advantage of being logistically and operationally similar to the Mirage 2000, which the IAF already operates and used with great success during the Kargil War (see Operation Safed Sagar). This would require fewer changes in the existing infrastructure of the IAF, which in turn will reduce cost. Moreover, being 100% French also provided Dassault a distinct edge over its competitors on the issue of technology transfer.
Dassault claims that the Rafale has an advantage over many of the competitors because it is not subject to ITAR restrictions.
The French government has cleared full technology transfer of the Rafale to India, including that of the RBE2-AA AESA radar which will be integrated into the Rafale by 2010
and also the transfer of software source codes, which will allow Indian scientists to re-programme a radar or any sensitive equipment if needed.
Without the software source codes, the IAF would have to specify mission parameters to foreign manufacturers to enable configuration of their radar, seriously compromising security in the process.
Dassault has also offered to fit the GTX-35VS Kaveri engine into the Rafale, which if chosen, would greatly improve commonality with the HAL Tejas that will enter service into the IAF by 2010. Concerns have been raised about cost issues as well as potential sales to Pakistan, which has also expressed interest in the Rafale. However, no such jets have been sold to Pakistan. India and France have recently agreed to "go beyond a buyer-seller relationship".
Eurofighter Typhoon

Eurofighter Typhoon
The Eurofighter Typhoon is a twin-engine multi-role canard-delta strike fighter aircraft, designed and built by a consortium of European aerospace manufacturers through Eurofighter GmbH.
Eurofighter is offering the Tranche-3 Typhoon for the Indian requirement, equipped with the CAESAR AESA radar. EADS has invited India to become a partner of the Eurofighter Typhoon programme if the Typhoon wins the contract, and will be given technological and development participation in future tranches of the Typhoon.
Bernhard Gerwert, CEO of EADS Defense Department, elaborated that if India becomes the fifth partner of the Eurofighter programme, it will be able to manufacture assemblies for new Eurofighters.
In January 2010, EADS offered to include thrust vectoring nozzles (TVNs) with the Typhoon's EJ200 engines for India. Thrust vectoring will improve operational capabilities, and reduce fuel burn by up to 5% and increase thrust while supersonic cruising by 7%.
Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet

F/A-18F Super Hornet
The Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet is a twin-engine carrier-based multirole fighter aircraft. The MMRCA contract represents a prime opportunity for U.S. defence companies to gain a foothold in the Indian defence market, which is estimated to be about
US$100 billion in the next 10 years. Initially, the Request for Information (RFI) was not issued to Boeing, which decided to field the Super Hornet. The U.S. Government allowed Boeing to participate in the RFI, and later gave permission for RFP (Request For Proposal) as well. However, any sale of aircraft would have to be approved by the U.S. Congress.
Initial reactions within the IAF were enthusiastic, although there were apprehensions of support issues in case of future sanctions. The US stated that there would have been some restrictions and pre-conditions for the purchase of the aircraft.
On 24 April 2008, Boeing (through the U.S. Embassy in New Delhi) submitted their 7000-page proposal to the Ministry of Defence, before the 28 April deadline for the submission for proposals. The Super Hornet variant being offered to India, the F/A-18IN, is based on the F/A-18E/F model flown by the U.S. Navy and currently being built for the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). Raytheon's APG-79 AESA radar was offered on the aircraft. There would have been limited Transfer of Technology on the radar, up to the level approved by the US Government. However, Raytheon stated that the level of ToT offered would be compliant with the RFP requirements.
Delivery of the first F/A-18IN Super Hornets could have begun approximately 36 months after contract award.
Boeing proposed joint manufacture of the jets with Indian partners. It also planned to offset the cost by setting up a US$100 million maintenance and training hub in Nagpur. This is the first time the Super Hornet has been offered for production in a foreign country.
On 14 February 2008, Boeing and Tata Industries agreed to form a joint-venture company. The new entity formed in February 2008, will supply components for Boeing military aircraft, including the Super Hornet.
In order to satisfy its offset requirements, Boeing has signed long-term partnership agreements with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), Tata Industries, and Larsen & Toubro.
Lockheed Martin F-16IN Super Viper
India initially sent the RFI for a F-16C/D Block 52+ configuration aircraft. On 17 January 2008, Lockheed Martin offered a customized version of the F-16, the
F-16IN Super Viper for the Indian MMRCA contract.
The F-16IN, which is similar to the F-16 Block 60, will be a 4.5 generation aircraft. Lockheed Martin has stated that it will be the most advanced F-16 variant developed. It will be more advanced than the F-16 Block 52s that the Pakistan Air Force has acquired.
Lockheed Martin described the F-16IN as "the most advanced and capable F-16 ever." Based closely on the F-16E/F Block 60 as supplied to the UAE, the features on the F-16IN include:
- Conformal Fuel Tanks (CFTs) – This will give the F-16IN a combat range of 1700 km with 1500 kg weapons load.
- A Northrop Grumman AN/APG-80 AESA (active electronically scanned array) radar. This is the same radar in service on the F-16 Block 60s in service in UAE.
- General Electric F110-132A engine with 143 kN full reheat thrust with FADEC Controls.
- Electronic warfare suites and infra-red searching.
- Advanced all-color glass cockpit.
- Helmet-mounted cueing system.
Lockheed Martin offered to sell India the F-35 Lightning II aircraft in the future, as replacements, if the F-16 was chosen.
The capabilities of the F-16 appear to be similar to the Mirage 2000s that the IAF currently operates. The F-16 is also more prone to pilot errors than the Mirage 2000H, which would also work against the F-16.
Mikoyan MiG-35
The
Mikoyan MiG-35 (Russian:
Микоян МиГ-35) (NATO reporting name
Fulcrum-F) is the production version of the latest MiG-29 and incorporates mature development of the MiG-29M/M2 and MiG-29K/KUB technology, such as glass cockpit and fly-by-wire technology. The IAF already operates MiG-29s, and the Navy has ordered MiG-29K/KUBs for its
INS Vikramaditya (formerly
Admiral Gorshkov) and INS
Vikrant-class aircraft carriers.
Russia unveiled the MiG-35 at Aero India 2007 in Bangalore, amid Moscow's keen interest to sell these planes to India. This was the first time that the final version of the MiG-35 was publicly displayed at an international air show, and thus, generated a great deal of interest.
Since the IAF already has maintenance and upgrade facilities for the MiG-29, this would mean that the fighter could be brought into service with a minimum of expenditure on infrastructure.
A major advantage of MiG-35 is that Russia is committed to transfer the plane's technology, including the new advanced Zhuk-AE Active Electronically Scanned Array radar, to India.
In the past, Russia has provided customised versions of military equipment such as the Su-30MKI and continued to provide support for equipment during international sanctions. However, Russian product support, especially for the MiG-29 fleet has been inadequate.
Additionally, buying the MiG-35 would mean an almost total dependence on a single supplier for India's entire fighter fleet. Recent Russian demands for renegotiation of earlier contracts, the sale of RD-93 engines (a variant of the Klimov RD-33 that powers the Indian MiG-29s) to Pakistan for its JF-17 Thunder aircraft and concurrently supplying combat aircraft to China
[42] has also caused concern in New Delhi.
Saab Gripen NG
The
Saab JAS 39 Gripen (
Griffin or
"Gryphon") is a fighter aircraft manufactured by the Swedish aerospace company Saab. The aircraft is in service with the Swedish, Czech, Hungarian and the South African air forces, and has been ordered by the Royal Thai Air Force.
The Gripen was one of the aircraft that the IAF sent the Request for Information. The Gripen participated at Aero India 2007, where one JAS 39C (single seater) and two JAS 39D (two-seater) variants were brought.
Gripen International offered the Gripen IN, a version of the Gripen NG (Next Generation) for India's competition.
The Gripen NG has increased fuel capacity, more powerful powerplant, higher payload, upgraded avionics and other improvements.
Aircraft shortlisted
It was reported on 27 April 2011 that only Eurofighter Typhoon and Dassault Rafale made the cut to the shortlist.
Eurofighter and Dassault have been told to keep their commercial bids open till 31 December 2011.
The US ambassador in India, Timothy Roemer said that they were “deeply disappointed” by the news, but added that they were reviewing the documents received from the Government of India and were “respectful of the procurement process”. He also said that the US looked forward to continuing to grow and develop their defence partnership with India.
Officials from SAAB confirmed that the Gripen was not shortlisted but added that they were committed to the Indian market and continue their plans for growth and that they see large business opportunities in the aerospace, defence and security sectors in India.
A US diplomatic cable leaked by Wikileaks has brought forward the fact that US diplomats already held the view that Indian defense trade, in such important deals with the USA, will be subject to scrutiny, owing to the US maintaining a favorable military partnership with Pakistan and due to the sanctions that the US imposed on India after the Pokhran-II nuclear tests. Timothy Roemer, the US ambassador to India, said in an 29 October 2009 cable to Michele Flournoy, a top Pentagon official then about to visit India that "Our ability to seize the opportunities presented by this newly improved environment is limited by the commonly held view that the U.S. will not prove to be a reliable supplier of defense equipment".